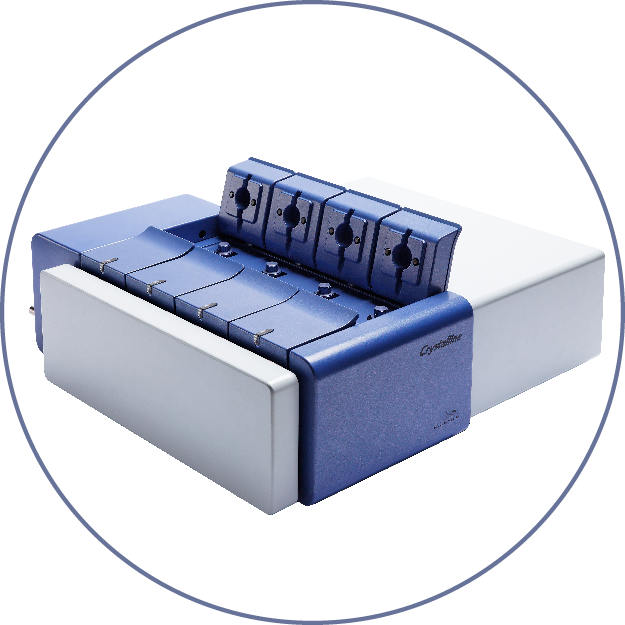
Parallel Crystallizers for Drug Development
- Home
- Automated Solutions
- Parallel Crystallizers for Drug Development
Parallel Crystallizers for Drug Development
Crystallization research plays an important role in the drug development process as majority of the therapeutic drugs exhibits in multiple polymorph forms and technically each polymorph possess different physical properties. Differences in physical properties (e.g. solubility, hygroscopicity, melting point) would then affect other important properties such as product bioavailability and stability. Pharmaceutical companies worldwide are now trying to gain their competitiveness by stepping in the crystallization research much earlier in the drug development cycle, thus to avoid unexpected crystal form related issues and delays at later stages. This also means crystal form information required during patent application could be obtained much earlier and eventually product launch could also be accelerated.
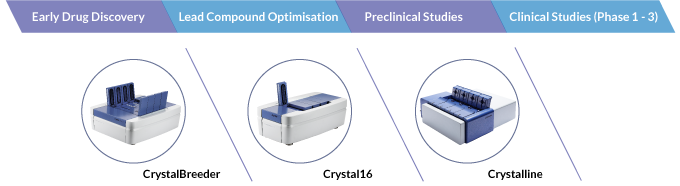
At the moment, the biggest bottleneck for crystallization research lies in the complex experimental matrix involved and the limited sample quantity. To tackle these issues, Technobis provides three innovative solutions and each of them can effectively perform polymorph screening, solubility and metastable zone width(MSZW) study and crystallization process research. Also, it comes with different features which can fulfil researchers’ needs such as throughput and processing volume at different development stages, and therefore effectively speeding up the entire crystallization research cycle.
Polymorph Screening
As the first step in crystallization research, polymorph screening typically involves screening of various salts, hydrates / solvates and co-crystals. In order to screen out all possible polymorphs and to identify the optimum crystal form for further investigations, it is necessary to perform screening with different solvent systems, counter-ions and co-compounds via different crystallization methods such as cooling, evaporation and slurry. This screening process is tedious and involves very diverse experimental conditions, researchers are advised to use the guide in Table 1 to select the most appropriate crystallizer.
| ? | CrystalBreeder | Crystal16 | Crystalline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor volume(mL) | 0.05 – 0.2 | 0.25 – 1.5 | 1 – 5 |
| Parallel channels | 32 | 16 | 8 |
| Individual temperature control module | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| Operating range(℃) | -15 to 150 | -15 to 150 | -25 to 180 |
| Crystallization methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling | √ | √ | √ |
| Evaporation | √ | – | √ |
| Vapor Diffusion | √ | – | √ |
| Anti-solvent | – | – | √ |
| (Crystal Seed) | – | – | √ |
The polymorph screening workflow is illustrated by Technobis CrystalBreeder as an example. Please mouse over to the workflow to view the corresponding steps.
 ?
? ?
? ?
? ?
? ?
?
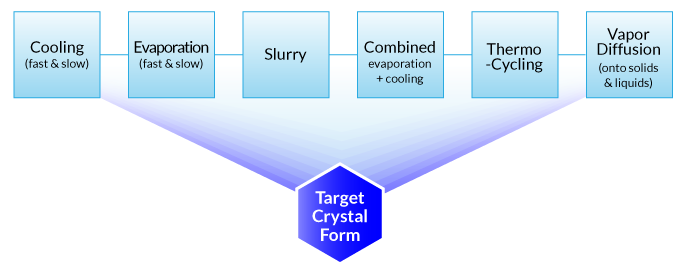
Fig 1. Crystallization modes of Technobis Crystalbreeder.
Solubility Curve and MSZW measurement
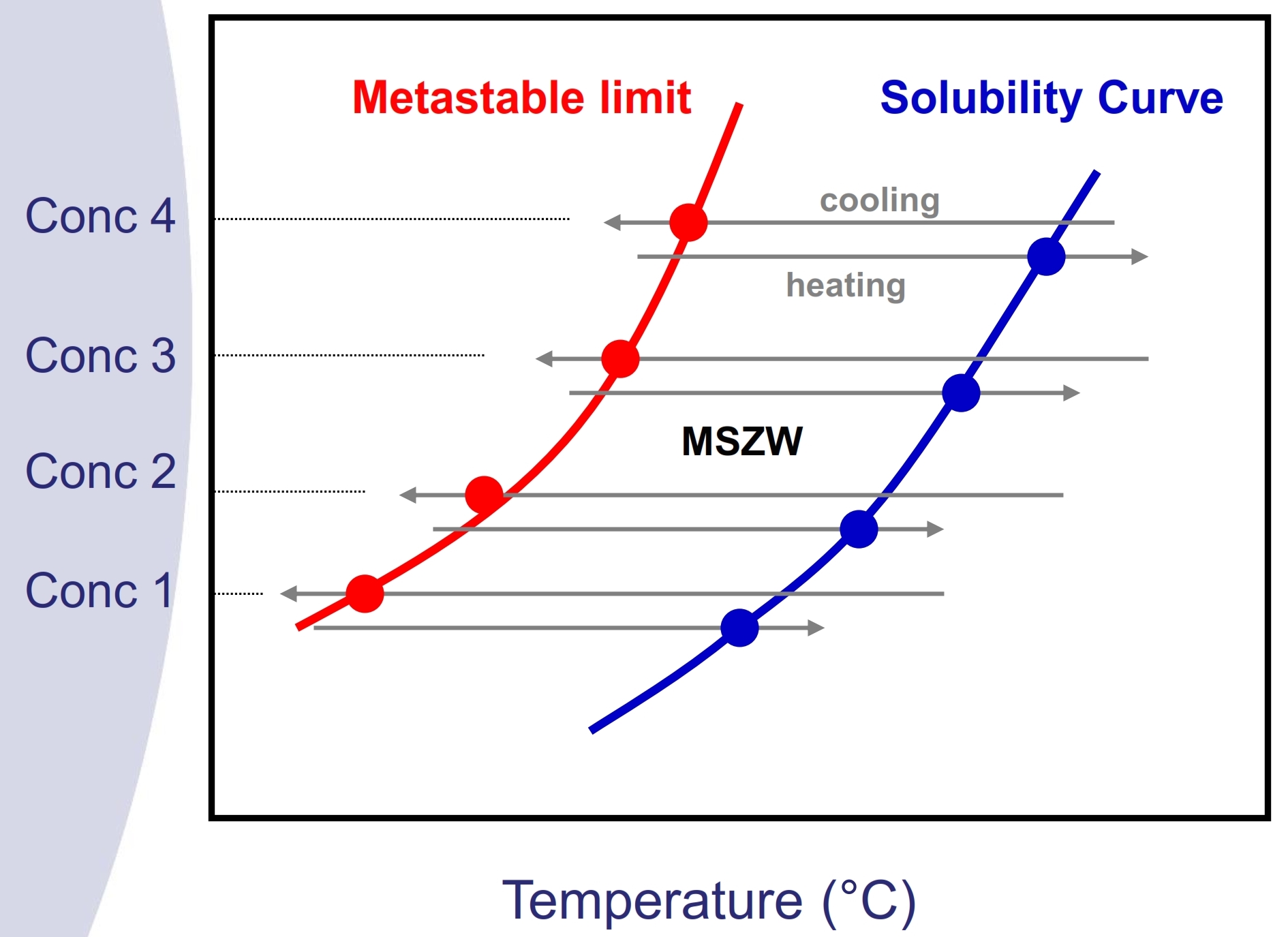
Fig. 2. Solubility curve and MSZW
Once the crystal form and solvent system have been selected, the next step would be to obtain the solubility curve and MSZW of the drug in the corresponding system, in order to identify the optimum operating range. Solubility and MSZW are both important data for a successful scale-up and to determine the right timing for seeding for an optimized process yield. Solubility study by conventional gravimetric approach is low in efficiency and frequently MSZW data are very difficult to obtain. On the other hand, Technobis systems can perform simple and efficient solubility curve and MSZW measurement by employing a non-invasive turbidity measurement approach together with precise temperature and stirring control.
| ? | CrystalBreeder | Crystal16 | Crystalline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor volume(mL) | 0.05 – 0.2 | 0.25 – 1.5 | 1 – 5 |
| Crystallization Method | Cooling, evaporation, vapor | Cooling | Cooling, evaporation, anti-solvent, gas vapor |
| Solubility Curve | 8 | 4 | 2 |
| MSZW Data | 8 sets | 4 sets | 2 sets |
The solubility & MSZW workflow is illustrated by Technobis Crystal16 as an example. Please mouse over to the workflow to view the corresponding steps.
 ?
? ?
? ?
? ?
? ?
?

Technobis Crystal 16 allows flexible experimental design as shown in the example in Figure 3. In this example, user could simply screen 4 solvents systems by preparing 4 concentrations of supersaturated solutions and by programming an appropriate heating/cooling profile. The system would then automatically detect the cloud point (point at which crystal first precipitates) and the clear point (point at which all suspended solids disappear). Users could immediately obtain 4 sets of solubility curves and MSZW graphs as they are directly generated by the CrystalClear software.
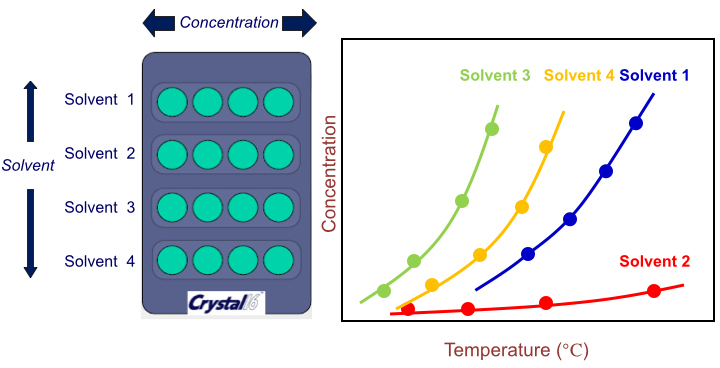
Fig. 3. Example the experimental design of a solubility study
Crystallization Process Development & Optimization
After selecting the right crystal form, researchers would optimize the crystallization process to ensure a good balance of crystal purity, particle size uniformity and process yield. Crystal purity and particle size uniformity are important properties which would significantly affect final dosage form formulation design, content uniformity, solubility, dissolution rate and eventually its bioavailability. With various online analysis options offered by Technobis parallel crystallizers, researchers could effectively perform efficient and comprehensive crystallization process optimization studies.
| ? | CrystalBreeder | Crystal16 | Crystalline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor volume(mL) | 0.05 – 0.2 | 0.25 – 1.5 | 1 – 5 |
| Crystallization method | Cooling, evaporation, vapour diffusion | Cooling | Cooling, evaporation, anti-solvent, vapour diffusion |
| In-situ Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidity | √ | √ | √ |
| Raman | – | – | √* |
| Camera | – | – | √* |
*Probes are purchased separately
Workflow
The crystallization process development & optimization workflow is illustrated by Technobis Crystalline as an example. Please mouse over to the workflow to view the corresponding steps.
 ?
? ?
? ?
? ?
? ?
?
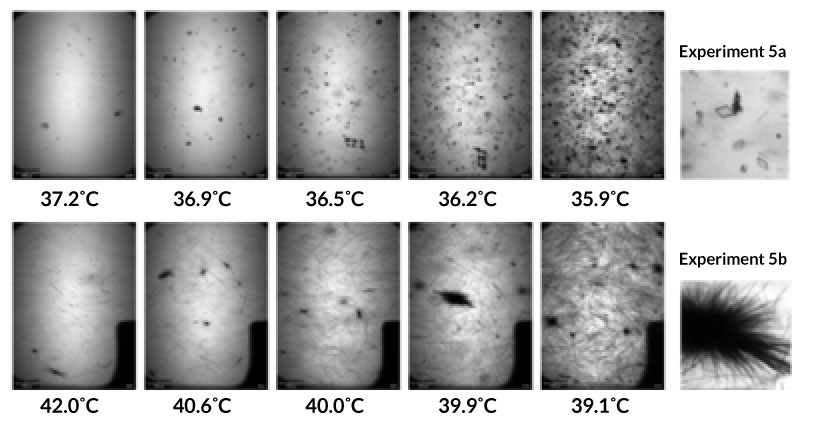
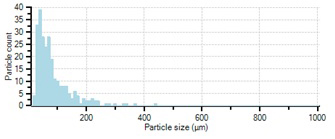
Fig. 5. Real-time particle size distribution
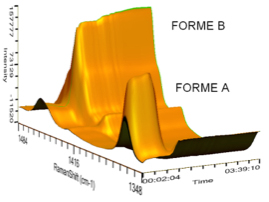
Conclusions
Technobis offers three compact-designed parallel crystallizers which are capable to perform comprehensive studies on polymorph screening and crystallization process optimization by effectively utilizing a limited amount of sample. It also rapidly transforms experimental data into valuable information and enhances research efficiency, thus becoming the ideal solutions for high throughput crystallization research.
 Technobis
CrystalBreeder
Technobis
CrystalBreeder